In the dynamic and competitive landscape of the panel industry, encompassing everything from plywood and MDF to particleboard and specialty engineered wood products, the demand for precision, efficiency, and safety has never been greater. As manufacturers strive to meet the ever-evolving requirements of high-quality output, shorter lead times, and stringent safety standards, robotic arms have emerged as the intelligent backbone of modern panel production lines. They are not merely automating tasks; they are fundamentally redefining the paradigms of efficiency, consistency, flexibility, and overall capabilities within the sector. By seamlessly taking over repetitive, strenuous, and often hazardous operations, robotic arms empower manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of productivity, product quality, and operational safety.
The true transformative power of robotic arms lies in their remarkable versatility and adaptability, enabling them to integrate seamlessly and intelligently across multiple critical stages of the panel manufacturing process, from raw material handling to finished goods packaging.
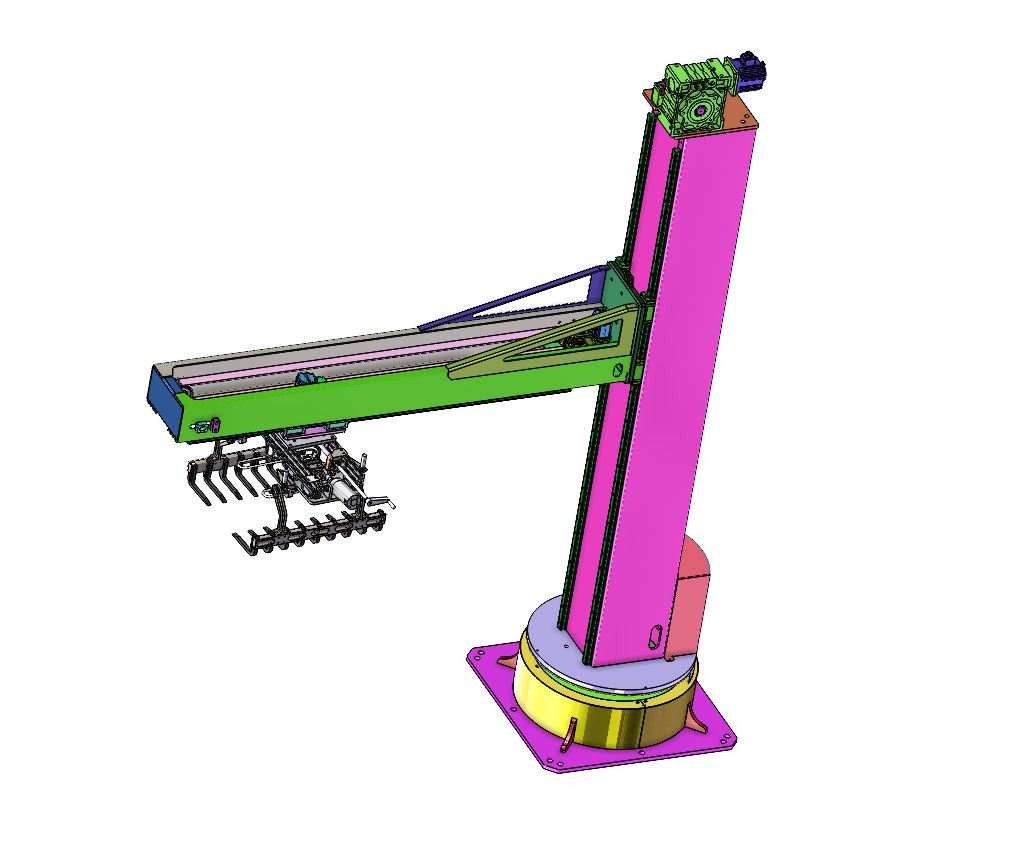
Intelligent Raw Material Handling and Stacking/Unstacking: At the very beginning of the production line, robotic arms equipped with advanced vision systems and sophisticated gripper technologies (ranging from vacuum suction cups for smooth surfaces to custom-designed mechanical fingers for textured or porous materials) provide a transformative solution for the often cumbersome task of handling large, heavy, and irregularly shaped panel stacks. They can safely, precisely, and efficiently pick up panels weighing anywhere from 10 kg to over 150 kg (with some heavy-duty models capable of handling even more), and place them onto infeed conveyors, sortation systems, or directly onto CNC machines and other processing stations. This capability extends to the end of the line as well, where robots expertly unstack finished panels, orienting them correctly and arranging them neatly for packaging, palletizing, or further inspection. This not only eliminates significant ergonomic risks for human workers but also ensures a consistent and gentle handling of panels, minimizing the risk of surface damage, scratches, or dents. Payload capacities of industrial robotic arms typically range from 20 kg to 250 kg, with reach (working radius) capabilities spanning from 1.4 meters to over 3.2 meters, easily accommodating a wide variety of panel sizes and weights. This allows for handling everything from narrow strips and cut-to-size components to large-format boards and panels.
Precision CNC Machine Tending and Load/Unload Automation: Loading and unloading Computer Numerical Control (CNC) routers, panel saws, edge banders, drilling machines, and other capital-intensive processing equipment is a high-risk, monotonous, and time-consuming task that is ideally suited for automation. Robotic arms perform this critical function with unwavering consistency, speed, and sub-millimeter precision. They can manage multiple machines simultaneously within a cell, intelligently feeding them with raw panels and retrieving precisely cut or machined pieces, drastically reducing machine idle time and maximizing Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). By eliminating the need for manual loading and unloading, cycle times can be reduced by up to 30% or more, effectively turning what was traditionally a batch-oriented process into a fluid, continuous, and highly efficient workflow. This level of integration minimizes production bottlenecks and significantly boosts throughput.
Automated Sanding, Finishing, and Surface Treatment: For finishing lines, articulated robotic arms are increasingly paired with force-sensing technology, advanced vision guidance, and specialized sanding or polishing tools. They can follow complex three-dimensional surface contours with micron-level precision, applying consistent and controlled pressure to deliver a flawlessly smooth, uniform finish. This is particularly valuable for high-gloss surfaces, laminates, or when preparing panels for painting or other coatings. The consistent application of pressure and the ability to navigate intricate profiles eliminate human variability, ensuring every panel meets the highest quality standards for surface finish. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the final product but also reduces material waste from inconsistent sanding, over-processing, or rework. The force control capabilities of these robots can be finely tuned to specific material types and desired surface finishes.
Component Assembly and Joinery: Beyond material handling and machining, robotic arms are also increasingly employed in the assembly of panel-based components, such as cabinet doors, frames, and modular furniture elements. They can accurately position and join panels using various techniques, including screwdriving, gluing, or inserting dowels and other fasteners. Vision-guided systems assist in precise part location and alignment, ensuring repeatable and high-quality assembly processes.
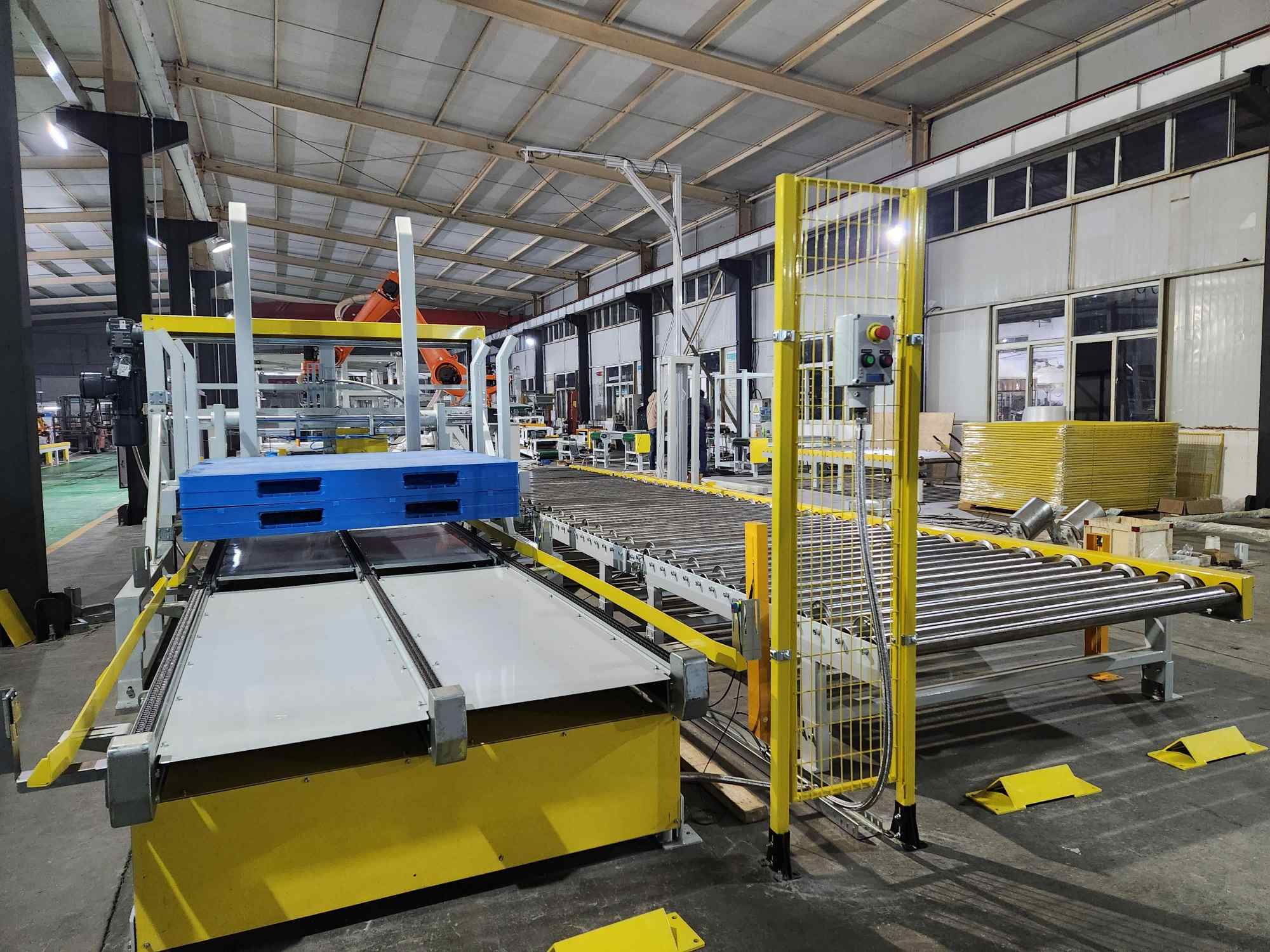

The deployment of robotic arms in demanding industrial environments, particularly those involving wood dust, variable panel densities, and potentially harsh conditions, is underpinned by robust and reliable technical specifications that ensure consistent performance, longevity, and safety.
Payload and Reach Capabilities: Industrial robotic arms specifically designed for panel handling applications typically feature payload capacities ranging from 20 kg to 250 kg, with some heavy-duty models offering even greater capacity. Their working radius (reach) spans from 1.4 meters to over 3.2 meters, providing the flexibility to access and manipulate panels in various orientations and from different angles within a production cell. This extensive range allows for handling everything from lightweight, narrow strips to large, heavy panels and boards.
Speed, Precision, and Repeatability: Equipped with high-resolution encoders, advanced servo motor technology, and sophisticated motion control algorithms, these robots operate with remarkable speed and agility. Their axis speeds can reach up to 200 degrees per second or more, enabling swift and responsive movements. Crucially, they offer exceptional repeatability, often as tight as ±0.05 mm to ±0.06 mm, ensuring that every action, from picking to placing, is executed with pinpoint accuracy. This level of precision is vital for maintaining tight tolerances in cutting, machining, and assembly operations.
Advanced End-Effector Versatility: The "hand" of the robot, or end-effector, is critically important and highly customizable. Grippers can be fitted with high-flow vacuum pumps capable of generating holding forces of hundreds of kilograms, ensuring secure handling of panels even on non-ferrous, smooth, or slightly porous materials like MDF, plywood, or laminated surfaces. For more delicate operations or when handling panels with uneven surfaces, softer foam pads, silicone grips, or sensor-integrated fingers provide gentle yet firm contact, preventing surface marring. Quick-change end-effector systems allow for rapid switchover between different tasks, enhancing the flexibility of the robotic cell.
Intelligent Software and Connectivity: The "brain" of the operation lies in the sophisticated control systems and software that power these robotic arms. Modern robotic arms run on intuitive programming interfaces, often featuring proprietary teach pendants for on-site programming or advanced offline programming (OLP) suites that allow for simulation and programming without disrupting production. They incorporate features like collision detection, path optimization, and adaptive control. Furthermore, they can be seamlessly integrated with factory MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), SCADA systems, and ERP platforms for real-time data tracking, production monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control, enabling a truly smart and connected manufacturing environment.
The strategic implementation of robotic automation in panel production translates directly into a formidable and quantifiable competitive advantage, impacting various aspects of the business.
Enhanced Productivity and Throughput: By operating 24/7 without breaks, fatigue, or the need for shift changes, robotic arms dramatically increase output capacity. A single robot can often replace 2-4 human operators in specific tasks, significantly boosting the overall throughput of the production line. This allows manufacturers to take on larger orders, reduce lead times, and respond more swiftly to market demands.
Uncompromising Quality and Consistency: Robots execute programmed tasks with unwavering consistency, eliminating the variability and potential for human error inherent in manual operations. This results in a significant increase in first-pass yield, a reduction in the number of rejects and reworks, and a consistently higher quality final product that meets exacting customer specifications. The precision and repeatability of robotic arms ensure that every panel is handled, processed, and finished identically.
Improved Workplace Safety and Risk Mitigation: Automating tasks that involve heavy lifting, repetitive motions, and close proximity to hazardous machinery (like CNC routers and saws) significantly reduces the risk of workplace injuries, including musculoskeletal disorders, cuts, and crush injuries. This creates a safer work environment, reduces absenteeism, and minimizes the potential for costly workplace accidents and associated liabilities.
Long-Term Cost Efficiency and Operational Optimization: While the initial investment in robotic automation is significant, the return on investment (ROI) is often realized within a reasonable timeframe through reduced labor costs, minimized material waste from errors and rework, lower scrap rates, optimized energy usage via streamlined workflows, and increased overall equipment utilization. Additionally, robots can perform tasks in environments that might be hazardous or uncomfortable for humans, further protecting the workforce and reducing insurance costs.
In conclusion, robotic arms are not just tools; they are the cornerstone of the smart factory and Industry 4.0 within the panel industry. They provide a powerful and proven synergy of strength, intelligence, precision, flexibility, and safety, turning the complexities and challenges of modern panel production into a streamlined, efficient, highly productive, and competitive operation. Embracing this transformative technology is not just about keeping up with the competition; it's about leading the industry forward into a new era of intelligent manufacturing.
Copyright By © Shandong Shine Machinery Co.,Ltd